Herpes Simplex
HERPES SIMPLEXDefinition of Herpes Simplex
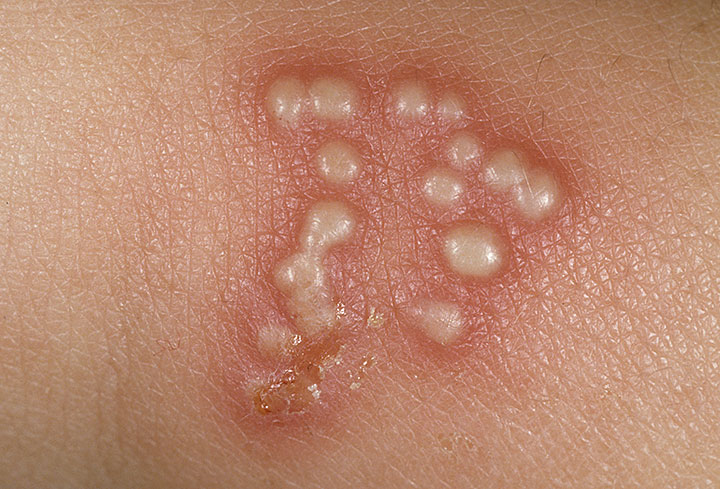
Herpes simplex refers to a group of viruses that infect humans. H. Virus infection simplex is characterized by vesicles clustered in the mucocutaneous with reddened skin. The disorder can occur in both primary and secondary. Herpes simplex causes painful wounds on the skin.
Cause of Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a common cause for injuries fever (cold sores) around the mouth. HSV-2 usually causes herpes sex. However, HSV-1 can cause genital infections, and HSV-2 can infect the mouth area through sex.
Clinical- Infection with this virus is characterized local primary lesions, latency and the tendency of local recurrence- 2 agents cause, HSV types 1 and 2, generally cause the clinical syndrome clear, depending on the entryHSV type 1:- Primary infection may be mild and usually occurs in childhood Early before the age of 5 years.- Approximately 10% of primary infections cause a more severe form of the disease manifesting fever and malaise.- It can last for a week or more, and is associated with vesicular lesions in the mouth, eye infection or a generalized skin eruption that aggravate chronic eczema.- Reactivation of latent infection results in cold sores that appear as clear vesicles on an erythematous base, usually on the face and lips, which berkrusta and recovered within a few days.- Reactivation may be caused by trauma, fever or an illness Another is being suffered.
HSV type 2:- The virus is the cause of genital herpes, although it can also be caused by virus type 1.- Genital Herpes occurs primarily in adults and transmitted Sexual- Primary and recurrent infections may occur, with or without symptoms.
Diagnosis of Herpes Simplex
Based on the clinical picture
ManagementTreatment of Herpes Simplex:- Therapy include:§ Idoksuridin for skin lesions§ ointment and povidone-iodine paint§ Acyclovir for initial and recurrent genital herpes, 5 times a day, 200-400 mg.§ i.v infusion acyclovir for encephalitis H. simplex and patients with immunosuppression.- Local Treatment for shingles should include cleaning wound with salt water and keep it dry. Gentian violet can be applied to the wounds.- The standard treatment for HSV is acyclovir in pill form to five time basis at the health center.